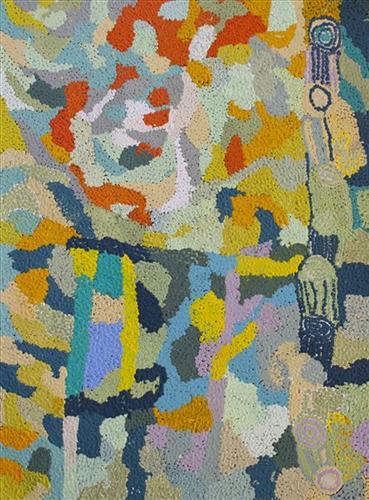111582001331
Waru (Fire)
“This a waru (fire). Nyurnma (freshly burnt) country there, and a waru-waru (green shoots and young plants). After that you got manguu (mature spinifex, able to be burnt).”
– Ngamaru Bidu
This work depicts the practice of fire burning as it continues to be used today through the Martu homelands. Over thousands of years, as Martu travelled and hunted on foot they would burn tracts of land, using waru as a means to assist with hunting, to encourage regenerative growth, and to increase biodiversity. Whilst fire burning practices have modernised in recent times, with Martu burning areas close to Aboriginal communities and along roads, or else further afield using helicopters and 4WDs with Indigenous ranger group Karnyirninpa Jukurrpa (KJ), the same objectives are met as those during pujiman (traditional, desert dwelling) times.
Targeted waru is an important tool in animal tracking. Small burns are lit to clear vegetation, expose burrows, and to allow for access to walk and track readily in exposed sands. Fires are typically burnt during cooler weather in small, controlled areas, reducing the risk of unmanageable, spontaneous bush fires whilst simultaneously providing diverse regenerating habitats. Remaining is a defined mosaic fire scar pattern in the land, across tali (sand dunes), linyji (clay pans), parulyukurru (spinifex country) and pila (sandy plains). This patterning is clearly visible in Ngamaru’s works, where she paints fire from an aerial perspective.
The patchwork nature of regrowth is aligned with the Martu cycle of burning and regrowth and its five distinct phases. First is nyurnma, followed after the rains by waru-waru, when young, bright green plants start to grow. Nyukura occurs between one and three years after burning, when plants have matured and are fruiting and seeding. Manguu is four to six years post burning, when spinifex has matured to the point that it can be burned once again. Finally, kunarka signifies the time when spinifex and other plant species have become old growth, and pose a risk of destructive bushfires.